Symptom & Risk for Gynecologic Cancers
There is no screening test for gynecologic cancer except the PAP smear for cervical cancer. Knowing the symptoms and your personal risk factors can save your life.
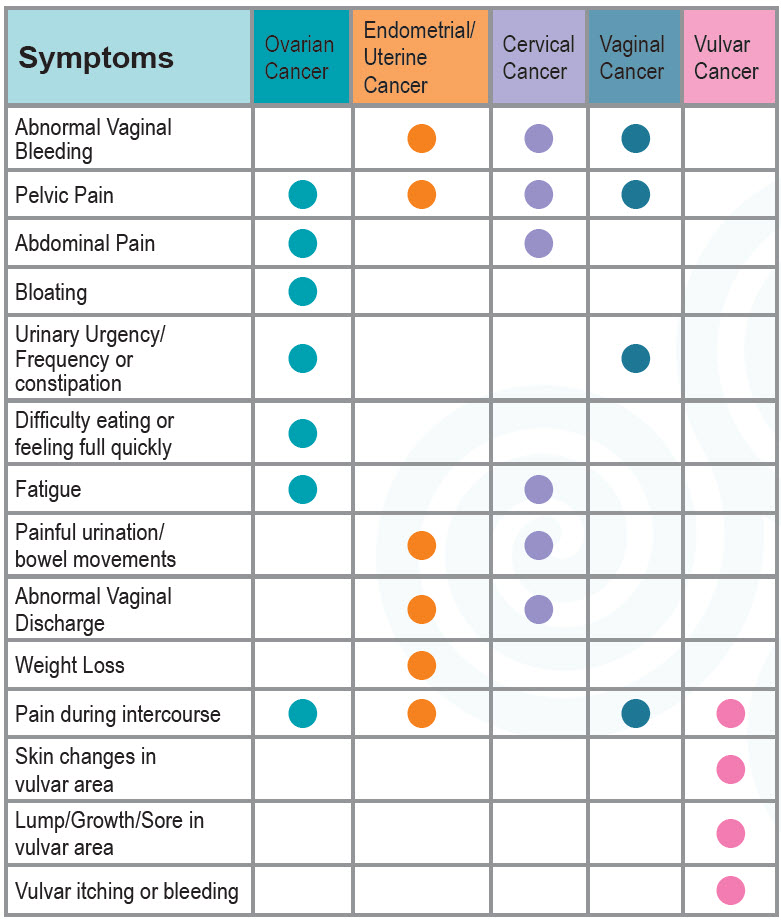
If you experience any of these symptoms almost daily for 2 or more weeks, talk to your gynecologist. If gynecologic cancer is suspected, insist on a referral to a Gynecologic Oncologist. Gyn-Onc’s are specialists in the diagnosis, surgery and treatment of gynecologic cancers. Studies show better outcomes when patients are treated by Gynecologic Oncologists.
Disclaimer: This information is designed to aid women in making decisions
about appropriate gynecologic care and does not substitute for evaluations with
qualified medical professionals familiar with your individual circumstances.
Risk Factors for Gynecologic Cancers
- Age: Over 55 at risk of ovarian, endometrial/uterine, vaginal & vulvar Cervical cancer is frequently diagnosed between 35 and 44.
- Family History: Close blood relative on either your mother’s or father’s side who had breast cancer before age Ovarian cancer, or male breast cancer at any age.
- Personal History: Cancer of the breast, ovary, uterus, colon, or rectum.
- Reproductive History: Never having children or having difficulty getting pregnant increases the risk for ovarian & endometrial/uterine cancer.
- Reproductive History: Both the use of birth control pills and giving birth to many children are associated with an increased risk of cervical cancer.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: If you have taken Hormone Replacement Therapy, you may be at higher risk.
- Disease: Having Diabetes, Polycystic Ovary
- Ethnicity: Persons of European and North American descent have a higher risk of ovarian cancer, as do Jewish people of Eastern European (Ashkenazi) descent.
- Endometriosis: If you have had a history of endometriosis, you are at a higher risk of ovarian cancer.
- Genetic Testing: Genetic testing indicating you have BRCA 1 or 2, or Lynch Syndrome, also known as HNPCC, puts you at a much higher risk for ovarian and endometrial/uterine cancers.
- Obesity: Being obese can put you at higher risk for some types of ovarian cancer & endometrial/uterine cancers.
- HPV: High-risk HPV infection causes cervical
- Sexual Activity: At a young age, especially before age 18, or having multiple sexual partners, are more likely to become infected with a high- risk type of HPV.
- DES exposure: People whose mothers took diethylstilbestrol while pregnant have an increased risk of cervical and vaginal cancers.
Having a risk factor for gynecologic cancer does not necessarily mean that you will get cancer. If you have risk factors, please talk to your doctor.
